Is it wise to consolidate debt with a mortgage? That’s a question on the minds of many in Canada as we navigate the complexities of personal finance. In our previous blogs, we’ve delved into the intricacies of debt consolidation and bridge finance. Now, it’s time to explore a strategy that’s becoming increasingly popular: using your mortgage to consolidate debts.
Often referred to as a debt consolidation mortgage, this method can greatly simplify your financial management. Not only does it streamline your debts, but it can also be a savvy move to reduce interest rates, potentially steering you back toward financial stability. In today’s blog, we’re going to unpack how debt consolidation through a mortgage works, its advantages, and important considerations before you dive in.
What is Debt Consolidation Through a Mortgage?
Think of your various debts — credit cards, personal loans, car payments — as a cacophony of different birds, each with its distinct chirp (interest rate) and flying pattern (payment schedule). Now, imagine gathering all these birds into one large, quiet aviary. That’s debt consolidation through a mortgage. It’s about combining all your smaller, high-interest debts into one larger debt — usually your mortgage — often with more favourable terms, like a lower interest rate. By adopting this strategy, you’re essentially streamlining your financial situation. Instead of juggling several different payments, you consolidate them into a single one. This could lead to substantial cost savings in the long run. Take this for instance: while your credit card might hit you with a steep 19% interest rate if you’re in Canada, a mortgage rate might just hover around 3% to 4%.
Let’s put this into a real-world scenario. Imagine you’ve got a $200,000 mortgage, owe $20,000 on your car, and have racked up $10,000 on your credit cards. What you can do is fold all these debts into your mortgage through debt consolidation. This bumps up your mortgage to $230,000. But here’s the kicker: the lower interest rate on your revamped mortgage could end up saving you a heap of cash in interest over time. There are two common techniques in Canada:
- Home Equity Loan for Debt Consolidation: This is done by borrowing against the equity in your property. If your home is worth $300,000 and your current mortgage balance is $200,000, you have $100,000 in equity. You can borrow some of your equity to pay off other high-interest debts.
- Refinancing to Consolidate Debt: This means replacing your existing mortgage with a new, larger one, covering both your original mortgage and your other debts. This new mortgage is set up at the current interest rates, which could be lower than what you were initially paying, and it streamlines all your debts into one payment.
Benefits of Consolidating Debts with a Mortgage
Consolidating your debts into a mortgage offers several advantages that can significantly ease your financial burden. Let’s take a closer look at these benefits, each with its own set of advantages and real-life applications:
- Lower Interest Rates: One of the biggest perks of rolling your debts into your mortgage is the chance to benefit from lower interest rates. Generally, mortgages come with rates that are way more forgiving than what you’d find with credit cards or high-interest personal loans. Picture this: you’re dealing with credit card debt at a whopping 20% interest, and on top of that, a personal loan charges you 15%. Now, imagine shifting both of these into a mortgage sitting pretty at just 4% interest. The amount you could save here is pretty significant.
- Single Payment: Imagine replacing several monthly payments – each with its own due date, interest rate, and terms – with just one. Consolidating your debts into a mortgage turns multiple obligations into a single monthly payment. This not only simplifies your financial management but also reduces the mental stress of keeping track of multiple bills. It’s easier to budget when you have one predictable payment each month.
- Improved Credit Score: Consolidating debts can also positively impact your credit score. By paying off multiple debts and reducing your credit utilization ratio, you may see an improvement in your credit rating. This is important for future borrowing and can open up more favourable lending opportunities.
- Tax Deductible Interest: In some cases, the interest you pay on a mortgage used for debt consolidation might be tax-deductible. This is not typically the case with credit card or personal loan interest. For homeowners who itemize deductions, this can be an added financial benefit.
- Flexible Repayment Terms: Mortgages offer flexibility in terms of repayment. You can often choose between a variety of term lengths and repayment options to suit your financial situation. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial for managing cash flow and budgeting.
- Access to More Funds: If the value of your house has increased, debt consolidation with a mortgage may provide you with access to a bigger sum of money than other types of loans. This is especially advantageous if you have a lot of high-interest debt.
- Stabilized Interest Rates: Choosing a fixed interest rate for your mortgage protects against potential interest rate hikes, unlike credit cards and variable-rate loans. This stability can offer peace of mind and assist in long-term financial planning.
Considerations and Risks
While consolidating debts with a mortgage offers several benefits, it’s equally important to understand the potential downsides and risks involved. Here are some critical considerations to keep in mind before proceeding with this financial strategy:
- Secured Debt: Unsecured debts (such as credit card bills or personal loans) become secured against your house when you consolidate them into your mortgage. This means that if you have difficulty paying payments, you are more likely to lose your home. It’s crucial to be confident in your ability to meet these new payment terms before securing additional debts against your home.
- Long-Term Costs: While consolidating loans into a mortgage can reduce monthly payments, it typically increases the time it takes to repay your debts. As a result, you may end up paying more interest during the loan’s life. Adding $20,000 in credit card debt to a 25-year mortgage, for example, may reduce monthly payments while increasing the total interest paid over time.
- Fees and Penalties: Refinancing a mortgage to consolidate debt can incur various fees, such as appraisal fees, legal fees, and administrative costs. Additionally, there might be penalties for breaking your current mortgage agreement. These costs can add up, so it’s important to factor them into your decision.
- Potential for More Debt: There’s a risk of falling into a debt cycle. If you consolidate your debts but don’t address the spending habits that led to the initial debt, you might find yourself accumulating new debts on top of your consolidated loan.
- Variable Interest Rate Risks: If you choose a mortgage with a variable interest rate for debt consolidation, be aware that your interest costs could increase over time with market fluctuations. This can lead to higher payments in the future, impacting your financial planning.
- Equity Reduction: Consolidating other debts into your mortgage reduces the equity you have in your home. This could limit your future capacity to access home equity for other purposes, such as home improvements or emergency money.
- Tax Implications: While mortgage interest is sometimes tax deductible, this does not necessarily apply to the amount of the mortgage utilized for debt consolidation. Understanding the tax implications is crucial to ensure that you’re making a financially sound decision.
Making the Right Choice
Before consolidating debts with a mortgage, it’s important to consider your personal financial situation and long-term goals. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and help you understand the best practices for debt consolidation with a mortgage.
Consolidating debts with a mortgage can be a smart strategy for some Canadians. It offers the convenience of a single payment and potential interest savings. However, it is critical to balance the benefits with the hazards and long-term effects. Debt consolidation through a mortgage can be a step toward financial stability and peace of mind with proper preparation and rigorous financial management.
FAQ
-
Can I use my mortgage to consolidate debt?
Absolutely. Many Canadians are turning to their mortgages as a means to consolidate various debts, like credit card balances and personal loans. This involves combining these smaller, high-interest debts into your mortgage, often benefiting from lower interest rates and a single payment.
-
Can I use a mortgage to pay off debt?
Yes, using a mortgage to pay off debt is a common strategy. This is done by either taking a home equity loan against the equity in your property or refinancing your mortgage to cover both your original mortgage and other debts, leading to potential interest savings.
-
Can I refinance my mortgage to pay off debt?
Refinancing your mortgage to pay off debt is a viable option. This process involves replacing your existing mortgage with a new, larger one, encompassing both your initial mortgage and your additional debts. This could result in a lower overall interest rate and a single, manageable payment.
-
What are the benefits of a mortgage loan for paying off debt?
The benefits include lower interest rates compared to unsecured debts, a single monthly payment for ease of management, potential tax deductions on interest, and improved credit scores by consolidating multiple debts.
-
How do debt consolidation and mortgage rates correlate?
Debt consolidation can often offer lower mortgage rates compared to the rates of credit cards or personal loans. This can lead to significant interest savings over time, making it a financially savvy move for many.
-
What does using home equity to consolidate debts involve?
Using home equity to consolidate debts involves borrowing against the equity in your home to pay off high-interest debts. This can be an effective way to manage and reduce your overall debt burden.
-
What are some best practices for debt consolidation with a mortgage?
Key practices include assessing your overall financial situation, understanding the long-term costs, being mindful of fees and penalties, and consulting with a financial advisor to ensure this strategy aligns with your financial goals.
-
Is mortgage refinancing to pay off debts a good idea?
Mortgage refinancing to pay off debts can be beneficial, but it’s important to consider the long-term implications, potential fees, and whether this aligns with your financial objectives
-
How does a debt consolidation loan compare to a mortgage?
A debt consolidation loan is specifically designed to consolidate debts and might offer different terms and rates compared to a mortgage. Mortgages generally have lower interest rates but could extend the debt repayment over a longer period.
-
Can you provide tips for successful debt consolidation with a mortgage?
Tips include understanding the terms of your new mortgage, maintaining discipline in not accruing additional debts, and regularly reviewing your financial status to ensure the strategy remains effective.
-
Are there specific mortgage lenders for debt consolidation?
Yes, some lenders specialize in debt consolidation mortgages. It’s advisable to shop around and compare offers to find the best terms suited to your financial situation.
-
How can a debt consolidation mortgage calculator be helpful?
A debt consolidation mortgage calculator can help you understand the potential savings, monthly payments, and the overall impact of consolidating your debts into a mortgage, aiding in informed decision-making.
Having already discussed benefits of debt consolidation, let’s move to another crucial financial strategy: bridge financing. Ever felt like you’re in a financial limbo, caught between the sale of your old home and the purchase of a new one? Bridge financing is the financial bridge that can get you from one side to the other with ease. Let’s learn more about bridge financing and how it can help you.
What is Bridge Financing and How Does it Work?
Bridge financing, commonly known as a bridge loan, is a short-term financing option used to bridge the gap between the immediate need for funds and the eventual availability of longer-term financing or resources. It’s often used in real estate transactions.
When you’ve sold your current home and are in the process of buying a new one, there might be a period where you need to pay for the new house before the funds from the sale of your old house are available. A bridge loan helps you cover the cost of the new home purchase during this interim period.
The bridge loan is secured by your existing home and is typically intended to be paid off with the proceeds from the sale of that home. This type of loan allows you to make the down payment on your new home and facilitates the transition between homes without the immediate cash from the sale of your old home.
It’s important to note that bridge loans are usually more expensive than conventional financing due to their short-term nature and the convenience they offer. They tend to have higher interest rates and may involve additional fees. Additionally, obtaining a bridge loan depends on the borrower’s creditworthiness and the equity in their current property.
Bridge Loan Interest Rates in Canada
Bridge loan interest rates in Canada can vary based on several factors, including the lender, the loan amount, the borrower’s credit score, and whether there is a sale agreement for the borrower’s old home.
As of late 2023, typical bridge financing rates were between 10.00% and 12.00%. These rates are generally higher than those for traditional mortgage loans because bridge loans are short-term and considered riskier by lenders. On average, bridge loan interest rates are around the prime rate plus 1%. Interest rates for bridge loans often hover around the Bank of Canada prime rate plus 2%, which would currently place them just over 9.2%.
Homeowners considering a bridge loan for a down payment should carefully review the interest rates offered by different bridge loan lenders and account for any additional fees, such as application and registration fees, to understand the full cost of the loan.
How Can I Qualify for a Bridge Loan?
Qualifying for a bridge loan in Canada typically involves the following criteria:
- Strong Credit Score: A good credit history is essential for approval.
- Equity: Significant equity in your current property is required, as the loan amount is often a percentage of this value, usually between 60-80%.
- Proof of Income: Lenders will require evidence of income to ensure that you can make the loan payments.
- Sale Timeline: A clear timeline for the sale of your current property is necessary.
- Lender Restrictions: Not all lenders offer bridge financing, and those that do may have specific restrictions.
- Property Type: While you can use a bridge loan for various property types, including rental properties, terms may differ if the property is not your primary residence.
The loan approval process can vary in duration, potentially taking anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. The bridge loan terms usually span from 6 to 12 months, though some lenders may extend up to 24 months. It’s also important to be aware of the higher interest rates and additional fees, like origination or closing costs, associated with bridge loans compared to traditional mortgages.
When Should I Consider Using a Bridge Loan?
You should consider using a bridge loan in the following situations:
- Home Purchase Overlap: If you’ve purchased a new home and your current home’s sale hasn’t closed yet.
- Seller’s Market: When you find your dream home in a competitive market and must act quickly.
- Closing Date Gap: There’s a short-term gap between the closing date of your new home and the sale of your old one.
- Cash Flow Management: To manage cash flow when you need immediate funds for a down payment.
- Avoiding Temporary Housing: To move directly into your new home without the need for temporary housing.
- Renovation and Sale: If you plan to renovate your new home before moving in, but need the funds from your current home’s sale to do so.
What are the Advantages of Bridge Loans Over Traditional Loans?
The advantages of bridge loans over traditional loans include:
- Timing Flexibility: They provide immediate cash flow, allowing for the purchase of a new property before the sale of an existing one.
- Convenience: Bridge loans can prevent the need for temporary housing and allow for a seamless move from one home to another.
- Strategic Financial Tool: They can be a strategic tool in a seller’s market, giving buyers the ability to make quick decisions and offers without sale contingencies.
- Short-Term Solution: Designed for short-term use, they typically do not have prepayment penalties if paid off early when the original property sells.
Finding the Right Lender and Determining Loan Amounts
When seeking out types of bridge financing, it’s critical to understand that not all lenders are created equal. You must find a lender that not only offers bridge loans but also one that aligns with your specific financial scenario. Whether you’re an individual transitioning between homes or a business in need of urgent capital, the lender should accommodate your needs with appropriate terms.
Understanding bridge loans means recognizing their diversity. Some lenders specialize in residential bridge loans, while others may cater to commercial clients, offering a bridge loan for business. Each comes with its own set of rules and qualification criteria.
For individuals, a bridge loan could be a percentage of your home’s value. In contrast, a bridge loan for a business might be based on the business’s cash flow or assets. Lenders will assess the risk and decide on the loan amount, typically ranging from 50-80% of the property’s value.
Short-term bridge loans are exactly that—short-term. They’re not a one-size-fits-all solution and should be chosen with a clear exit strategy in mind, as they generally carry higher interest rates and fees due to the urgency and flexibility they provide. The key is to find a lender that offers the most favourable terms for your short-term financial gap, with a clear understanding of the costs involved.
FAQs
How long does it take to get a bridge loan?
- It can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to get approved for a bridge loan, depending on the lender and the borrower’s qualifications.
Are there risks involved with bridge financing?
- Yes, risks include higher interest rates compared to traditional loans, the potential difficulty in selling the current home quickly, and the financial strain if the bridge loan’s term expires before the home is sold.
What are the differences between bridge loans and mortgages?
- Bridge loans are short-term, typically have higher interest rates, and are meant to be repaid quickly, often through the sale of a property. Mortgages are long-term with lower interest rates, spread over many years.
Can I use a bridge loan to purchase a new home before selling my current one?
- Yes, bridge loans are specifically designed for this purpose, allowing you to finance the purchase of a new home while awaiting the sale of your current one.
How do lenders determine the amount of bridge financing I can receive?
- Lenders look at the equity in your current home, your credit score, income, and the value of the new property to determine the loan amount, which is typically a percentage of your current home’s value.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by multiple debt payments with their sky-high interest rates? Debt consolidation might just be the life raft in the tumultuous sea of your finances. This financial strategy is akin to a conductor harmonizing the orchestra of your debts into a single, mellifluous symphony. We’ve already navigated the complexities of debt consolidation and bridge financing; now, let’s answer the question: What are the benefits of debt consolidation?
What is Debt Consolidation?
Debt consolidation is a financial strategy that involves combining multiple debts—be they credit card balances, medical bills, personal loans, or other lines of credit—into one consolidated loan. This can often result in a single monthly payment instead of multiple payments to different creditors, and potentially, a lower overall interest rate.
Imagine your debts as a crowd of chattering voices, each clamoring for attention. Debt consolidation acts as a unifier, bringing all those voices into a single, clear conversation. Top 10 Benefits of Debt Consolidation
Let’s delve into the benefits of debt consolidation and understand how it can streamline our financial wellbeing.
1. Simplified Finances: One of the Prime Debt Consolidation Benefits
Combining multiple debt obligations into a single payment is a key advantage of debt consolidation, especially relevant in Canada where juggling several debts is common. This convenience is not just about ease; it’s a strategic move that reduces the chances of missed payments and the negative impact they can have on your credit score, a cornerstone among the benefits of merging debt.
2. Lower Interest Rates: A Top Advantage of Consolidating Debt
In Canada’s varied financial landscape, consolidating debt can often secure a lower interest rate across the board, replacing high-interest credit card and loan rates. This can lead to considerable savings on interest payments, a driving force behind the debt consolidation perks and advantages.
3. Fixed Repayment Schedule: A Clear Debt Consolidation Perk
A fixed repayment schedule that comes with a consolidation loan provides a clear payoff timeline. This is a profound advantage for Canadians, making the path to debt freedom transparent and attainable, and is a hallmark reason for debt consolidation.
4. Lower Monthly Payments: A Financially Strategic Debt Combination Advantage
The benefits of merging debt include the possibility of reduced monthly payments. For Canadians, this can mean freeing up income for other expenses or investments. Although this may extend the term of the debt, the immediate cash-flow relief is a significant pro of debt consolidation.
5. Avoiding Late Fees: An Overlooked Debt Management Benefit
The consolidation of debts into a single payment simplifies the payment process, significantly reducing the likelihood of incurring late fees, a particular advantage in the Canadian financial context where such fees can be hefty. This is one of the practical debt consolidation perks and advantages that can help maintain a healthier credit score.
6. Psychological Benefits: The Emotional Perk of Debt Consolidation
Debt stress is real and can be debilitating. In Canada, consolidating debts can offer a psychological boost, with the knowledge that you are taking control of your finances. This mental and emotional relief is among the most significant, yet intangible, consolidating debt advantages.
7. Credit Score Improvement: A Fundamental Benefit of Merging Debt
In Canada, where a good credit score is crucial, the consistent on-time payments made possible through debt consolidation can improve your credit score over time. This is a long-term benefit of debt consolidation, fostering a healthier financial future.
8. Stopping Collection Calls: An Immediate Advantage of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation can provide immediate relief from the relentless pressure of collection calls, a common problem for Canadians with overdue debts. This cessation is a direct debt repayment benefit, allowing for peace of mind and the ability to focus on the future.
9. Budgeting Assistance: A Key Debt Consolidation Perk
For Canadians, a single debt payment through consolidation means a more straightforward budgeting process. This helps in creating a clear financial plan, which is an important debt management benefit, encouraging more responsible financial behavior.
10. Long-Term Financial Health: The Strategic Goal of Debt Consolidation
The structured payment plan of a debt consolidation loan is geared towards setting Canadians on the road to improved financial health. This strategic advantage of consolidating loans not only aids in managing current debts but also lays the foundation for a debt-free future, the ultimate financial goal for many.
Debt Consolidation Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding how debt consolidation helps can be the key to unlocking a more manageable financial situation, but it’s equally important to be aware of potential missteps along the way. When consolidating debts, one of the primary mistakes to avoid is not researching enough to secure the best interest rate possible, which can lead to insufficient savings or even higher costs over time. Another common error is extending the loan term too much, which, while lowering monthly payments, can result in paying more interest in the long run. Additionally, overlooking fees associated with setting up new loans or missing the underlying issue of spending habits can sabotage the benefits of consolidation. To navigate the debt consolidation process successfully, it’s crucial to compare different consolidation options, thoroughly understand the terms and conditions, and have a clear repayment strategy in place. This proactive approach ensures that the consolidation serves its purpose—simplifying your payments and reducing the cost of your debt.
In wrapping up, consolidating loans emerges as a beacon for those adrift in financial tumult. It orchestrates a unified approach to debt, delivering lower interest rates, a single payment schedule, and the relief of a fixed repayment plan. For Canadians navigating these waters, the strategy offers a clear route to financial stability. With careful planning and mindful avoidance of common pitfalls, the advantages of consolidating loans can harmonize one’s financial life, setting a course towards the tranquility of being debt-free.
FAQ
How does debt consolidation help with finances?
Debt consolidation helps by combining multiple debt payments into one, often with a lower interest rate. This simplification can lead to reduced monthly payments, easier budget management, and a clearer path to paying off debt, which can improve overall financial health.
Why consider debt consolidation for multiple debts?
Consolidating multiple debts can streamline your payment process, reduce the stress of managing various accounts, and potentially lower your overall interest rates. It also helps in avoiding missed or late payments, which can negatively impact your credit score.
What advantages come with merging debts?
Merging debts through consolidation typically offers the advantage of a lower interest rate, a single monthly payment, and a fixed repayment term. These factors combined can provide clarity, ease of payment, and potential savings on interest charges.
What are the perks of using debt consolidation services?
Using debt consolidation services can provide professional guidance, access to better interest rates, and a structured repayment plan. Services may also negotiate with creditors on your behalf and assist in tailoring a consolidation plan that fits your financial goals.
Recent data from the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC) reveals a concerning trend. The number of Canadian homeowners with a mortgage reporting an increase in debt has risen significantly, from 31.6% to 47.7%, representing an alarming increase of 16.1 percentage points. This substantial increase underscores the financial challenges many Canadians face.
Building on the insights we previously explored in our guide, “Comprehensive Mortgage Solutions,” we will now delve into debt consolidation and bridge financing as effective strategies to manage these challenges. We will examine their benefits, processes, and when they should be considered, providing insights to help Canadians better navigate their financial situations and alleviate debt-related stress.
What is Debt Consolidation?
Debt consolidation is a powerful financial strategy designed to help individuals regain control over their financial situations by merging a variety of debts into a single, more manageable obligation. These debts typically include credit card bills, personal loans, and various other unsecured financial obligations. What distinguishes debt consolidation from traditional loans is the often-integrated aspect of collateralization. In many cases, valuable assets, such as a mortgage or other property, are used as collateral to secure the consolidated debt.
The central objective of debt consolidation is two-fold: to curtail the overall interest rates incurred on multiple debts and to streamline the often convoluted landscape of monthly payments.
Benefits of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation offers several advantages, including:
- Lower Interest Rates: One of the most compelling benefits of debt consolidation is the potential to secure a lower interest rate. In most cases, the interest rate on a debt consolidation loan or line of credit is notably lower than the rates associated with high-interest credit cards or other unsecured debts. This can lead to substantial savings over time, reducing the overall cost of borrowing and making it more cost-effective to pay down existing debts.
- Simplified Finances: Managing a multitude of debts with varying due dates, interest rates, and terms can be overwhelming and confusing. Debt consolidation streamlines your financial obligations by consolidating them into a single, more manageable loan. This means you’ll only need to make one monthly payment, typically at a lower interest rate, greatly simplifying your financial life. This simplification not only eases the administrative burden but also offers a clearer perspective on your financial progress.
- Potential Credit Score Improvement: Timely payments on a consolidated debt can have a positive impact on your credit score. When you consistently make on-time payments on a single, consolidated loan, it demonstrates financial responsibility and reliability to credit reporting agencies. This can gradually enhance your credit score, making it easier to access credit at more favourable terms in the future.
- Fixed Repayment Schedule: Debt consolidation loans come with a fixed repayment schedule, which provides structure and predictability to your financial planning. Knowing exactly when your debt will be fully paid off enables you to create a solid budget and financial plan. This stability can reduce anxiety associated with fluctuating interest rates or uncertain debt repayment timelines.
- Reduced Stress: The burden of managing multiple debts, often with high-interest rates, can be a significant source of stress. Debt consolidation lightens this load by making your debt more affordable, which, in turn, reduces the mental and emotional strain associated with financial worries. Having a single, consolidated debt to focus on can offer peace of mind and financial stability.
- Debt Reduction: Debt consolidation allows you to actively reduce your outstanding debt. By consolidating high-interest debts, you may be able to pay off your obligations more quickly, saving you money on interest payments in the long run.
- Enhanced Financial Discipline: A consolidated debt typically comes with a fixed repayment schedule. This can help you develop and maintain better financial discipline, ensuring that you make consistent payments and reduce your debt steadily over time.
- Variety of Debt Types: Debt consolidation is versatile and can be applied to various types of debt, such as credit card debt, personal loans, medical bills, and more. It provides a holistic approach to managing multiple financial obligations.
Debt Consolidation Strategies
Debt consolidation can take various forms, depending on the individual’s financial situation. Strategies may include taking out a debt consolidation loan or consolidating debts through a mortgage. Let’s check the methods in details:
1.Debt Consolidation Loans: A Common Approach
One of the most common methods for consolidating debt is to obtain a debt consolidation loan, which can be secured from various financial institutions. This type of loan provides individuals with the means to pay off their existing debts by replacing them with a new, single loan. Debt consolidation loans are generally favourable due to their typically lower interest rates compared to the high rates often associated with credit cards, offering a more cost-effective and manageable option for those seeking to streamline their financial commitments and reduce overall interest expenses.
2. Consolidating Debts with a Mortgage
Debt consolidation often entails securing the consolidated debt with collateral, and one of the most common forms of collateralization is through a mortgage. Using a mortgage to consolidate your debts can provide several advantages. Here’s a closer look at the specific aspects of consolidating debts with a mortgage:
- Collateralization with a Mortgage: Debt consolidation frequently involves securing the consolidated debt with collateral, most commonly in the form of a mortgage. When you use a mortgage to consolidate your debts, it means that your home or property serves as the security against the loan. This form of debt consolidation is known as a home equity loan or a home equity line of credit (HELOC).
- Home Equity Loans (Second Mortgages): A home equity loan allows you to borrow against the equity you’ve built in your home. This type of debt consolidation typically offers a lump sum of money that you can use to pay off high-interest debts.
- Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC): A HELOC works more like a credit card, allowing you to borrow as needed up to a certain limit. This flexible option can be a practical choice for those who may not need to consolidate all their debts at once but want access to a revolving line of credit backed by their home’s equity.
- Risks of Using a Mortgage as Collateral: While using your home as collateral can lead to lower interest rates and favourable terms, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks. Should you be unable to make the payments on the consolidated debt, there’s a risk of losing your home.
- Consideration of Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio: Lenders typically evaluate the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio when offering home equity loans or HELOCs. This ratio represents the amount you owe on your mortgage compared to the current appraised value of your home.
3. Consolidating Debt with a Personal Loan
In some cases, Canadians may choose to use personal loans to consolidate their debts. These loans are unsecured, meaning they do not require collateral, and can be used to pay off various high-interest debts. However, they often come with higher interest rates compared to mortgage-based debt consolidation. Personal loans offer flexibility and may be preferred by individuals who don’t want to risk their assets but are willing to manage slightly higher interest costs in exchange for unsecured debt consolidation.
Are There Any Disadvantages to Debt Consolidation?
While debt consolidation can be a helpful financial strategy, there are potential drawbacks, including:
- Extended Repayment Period: Extending the repayment period may result in paying more interest in the long run.
- Risk to Assets: Secured debt consolidation, such as a mortgage, puts the associated asset at risk if payments are not made.
- Credit Score Impact: Initially, your credit score may drop, but it should recover as you make timely payments.
Now it’s time to speak about bridge financing.
How Bridge Financing Works
Bridge financing serves as a crucial financial solution within the realm of real estate transactions. Its primary function is to enable both homebuyers and real estate investors to bridge the temporal gap that often exists between the sale of an existing property and the acquisition of a new one. This unique financial tool facilitates the seamless transition from one property to another by providing the necessary funds during this critical interim period.
Bridge Loans
Bridge loans are specially crafted short-term financial instruments tailored to address this transitional challenge. Typically accompanied by slightly higher interest rates, these loans serve as a bridge between purchasing a new property before selling an existing one. The central purpose of bridge loans is to prevent homeowners from shouldering the financial burden of owning two properties simultaneously, thereby ensuring a smoother and more manageable transition within the real estate market.
Bridge Financing Process
The bridge financing process involves several essential steps:
- Assessment: Lenders meticulously assess the value of your existing property as well as your creditworthiness to determine the amount of bridge financing you qualify for.
- Loan Approval: Once your application is approved, you gain access to a bridge loan, equipping you with the financial means to secure your new property.
- Sale of Existing Property: After successfully selling your existing property, the proceeds generated from the sale are typically used to settle the bridge loan, ensuring a smooth transition without the financial burden of carrying both properties.
- Transition to a Mortgage: If the need arises, you can opt to transition from the bridge loan to a long-term mortgage, allowing you to structure your financial arrangements according to your specific needs and preferences after the sale of your previous property. This transition marks the completion of the bridge financing process, which has effectively facilitated your journey from one property to the next within the real estate market.
When Should I Consider Bridge Financing in Real Estate?
Bridge financing can be a valuable tool for:
- Homebuyers: Bridge Financing for homebuyers can be favourable when you want to buy a new home before selling your current one.
- Downsizing: When moving to a smaller property, bridge financing can help with the purchase before selling the larger one.
- Competitive Real Estate Market: In a competitive market, bridge financing ensures you don’t miss out on your desired property.
Bridge Financing for Real Estate Investors: Benefits of Bridge Financing in Real Estate
For real estate investors, bridge financing offers unique advantages, including:
- Swift Transactions: Investors can secure properties quickly, allowing for faster turnaround and potential profit.
- Portfolio Expansion: Bridge financing enables investors to acquire additional properties while they optimize existing ones.
- Renovation Funds: Investors can use bridge loans to fund renovations and improvements to increase property value.
Debt Consolidation vs. Bridge Financing
Debt consolidation and bridge financing are two distinct financial strategies with specific purposes. Debt consolidation primarily focuses on improving one’s overall financial health by combining multiple existing debts into a single, often lower-interest obligation. Its primary aim is to reduce interest rates, simplify monthly payments, and alleviate the burden of managing various debts.
In contrast, bridge financing is a short-term financing solution, frequently used in real estate transactions. It serves as a bridge between selling one property and purchasing another, typically through a short-term loan, allowing individuals to secure their new property before selling the old one.
While debt consolidation addresses the management of existing debts and long-term financial well-being, bridge financing is geared towards facilitating the smooth transition between real estate transactions, such as buying a new home before selling the current one. The choice between these strategies depends on an individual’s specific financial goals and circumstances.
Since we’ve already covered mortgage basics let’s now discuss mortgages in Manitoba. Imagine the pristine landscapes and vibrant communities of Manitoba, with their welcoming spirit beckoning you to become a part of their tapestry, as you step closer to homeownership in this picturesque province.
Whether you’re new to the mortgage world or have some prior knowledge, understanding the steps to qualify for a mortgage in Manitoba is vital on your journey to that perfect home. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the nuances of Manitoba mortgage qualification journey. So, let’s unravel the secrets to securing your dream home in this captivating province, where the tranquil beauty of the natural world meets the warmth of its communities.
We’ll answer the most frequently asked questions to give you a better understanding of the mortgage qualification.
How can I qualify for a mortgage in Manitoba?
Qualifying for a mortgage in Manitoba involves a multi-faceted evaluation by Manitoba mortgage lenders. These lenders typically consider your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and employment stability. The real estate market in Manitoba can also influence your qualifications, as competitive markets may require more robust financial profiles. To enhance your chances, consider following mortgage tips Manitoba experts recommend, such as improving your credit score or reducing existing debt. Other tips for helping you succeed include:
- Understand the Impact of Manitoba’s Seasonal Real Estate Market: Manitoba’s real estate market can be influenced by the seasons. In the spring and summer, more homes are typically listed, but prices may be higher due to increased demand. In contrast, the winter months might offer lower prices, but there could be fewer properties available. Understanding these seasonal variations can help you time your home purchase to align with your budget and preferences.
- Consider Pre-Approval for a Mortgage: Before you start house hunting in Manitoba, consider getting pre-approved for a mortgage. This involves working with a lender to assess your financial situation and determine the maximum loan amount you can secure. Pre-approval not only provides you with a clear budget but also makes you a more attractive buyer in the eyes of sellers.
- Budget for Property-Related Expenses: When purchasing a home in Manitoba, it’s essential to budget for all property-related expenses. Beyond the mortgage payment, consider costs such as property taxes, home insurance, and potential maintenance or renovation expenses. Having a comprehensive budget will help ensure you can comfortably afford your new home and meet your mortgage obligations.
What are the eligibility criteria for mortgages in Manitoba?
Eligibility criteria for mortgages in Manitoba are a critical aspect of the home buying process. While requirements may vary slightly between Manitoba mortgage lenders, there are some common factors that you should be aware of:
- Credit Score: What credit score do I need to get a mortgage in Manitoba?” is a common question among prospective homebuyers. Your credit score plays a significant role in mortgage qualification. To secure the best rates and terms, aim for a credit score above 650, which is often seen as a baseline requirement by Manitoba mortgage lenders. Regularly monitor Manitoba mortgage rate trends to gauge the optimal time for securing your mortgage. Additionally, a higher credit score can help you access low-interest mortgages in Manitoba, saving you money in the long run. To improve your credit score, make sure to pay bills on time, reduce outstanding debts, and avoid late payments or defaults.
- Stable Employment: Lenders want assurance that you have a stable source of income to cover your mortgage payments. Employment stability is crucial, so you’ll need to demonstrate a consistent work history. If you’re self-employed or have irregular income, you may need to provide additional documentation to prove your financial stability.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lenders assess your debt-to-income ratio, which is the percentage of your income that goes toward paying debts. Generally, a lower debt-to-income ratio is preferable, as it indicates that you have more disposable income to meet your mortgage obligations. To improve your debt-to-income ratio, consider paying down existing debts or increasing your income.
- Manitoba Home Buying Requirements: Manitoba has specific regulations and requirements for homebuyers. These may include property-related expenses such as property taxes and insurance. It’s essential to understand and budget for these additional costs when assessing your eligibility for a mortgage.
- Down Payment: While not a strict eligibility requirement, the size of your down payment can influence your mortgage approval and terms. A down payment ranging from 5% to 20% of the property’s purchase price is common in Manitoba. A larger down payment can help you secure a better mortgage rate and potentially avoid additional insurance costs.
- Manitoba Housing Market Analysis: The state of the housing market in Manitoba can also impact your eligibility for a mortgage. In a competitive market, you may need to act quickly and make strong offers to secure the home you desire. Understanding the current market conditions and the availability of housing options is crucial for successful mortgage approval.
To ensure you meet these eligibility criteria, it’s essential to evaluate your financial situation thoroughly. If your credit score is less than ideal, work on improving it by paying down debts and resolving any outstanding issues. Maintaining stable employment and managing your debt responsibly are crucial components of mortgage eligibility. Additionally, staying informed about the Manitoba housing market can help you make strategic decisions when it comes to your home purchase. Consulting with a mortgage broker in Manitoba can be beneficial in navigating the nuances of these eligibility requirements and connecting you with lenders who suit your financial profile.
How does income verification work for Manitoba mortgages?
Manitoba mortgage lenders require proof of stable income, typically through pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements. Accurate income verification is crucial to ensure you can meet your mortgage payments. Additionally, your employment history plays a vital role, with many lenders looking for a consistent work history of at least two years to establish your financial stability.
Are there government assistance programs for Manitoba mortgages?
Manitoba provides a range of government assistance programs to support first-time homebuyers and make the dream of homeownership more attainable. These programs can significantly alleviate the financial burden associated with buying a home, making it easier for individuals or families to enter the real estate market. Here are some of the key government assistance programs available in Manitoba:
- First-Time Home Buyer’s Tax Credit: This federal program provides a tax credit to first-time homebuyers in Manitoba. It allows you to claim a portion of your home purchase costs as a non-refundable tax credit when you file your annual income tax return. This can result in significant savings, making homeownership more affordable.
- Manitoba Housing Finance Program: Manitoba Housing offers various programs and services to assist low to moderate-income households in finding affordable housing. These programs often include rent subsidies, down payment assistance, and affordable mortgage options. Eligibility criteria for this program may vary, so it’s essential to review the specific details to see if you qualify.
- Land Transfer Tax Rebate: Manitoba offers a land transfer tax rebate to first-time homebuyers. This rebate allows eligible individuals to recover a portion of the land transfer tax they paid upon purchasing a property. The amount of the rebate can vary, so it’s important to check the current regulations and requirements.
- Home Buyer Assistance Program (RAP): The Home Buyer Assistance Program, administered by Manitoba Housing, provides financial assistance to low-income families and individuals to help with down payments and closing costs when purchasing a home. It’s an excellent resource for those who might face financial barriers to homeownership.
- Indigenous Housing Programs: Manitoba offers specific housing programs for Indigenous peoples and communities. These programs aim to improve housing conditions and affordability for Indigenous families in the province. Eligibility requirements for these programs can differ based on the specific program and community.
- Homeownership Programs for Specific Regions: Some regions within Manitoba offer their own homeownership programs, often tailored to the unique needs of the local community. These programs may include grants, subsidies, or low-interest mortgages, so it’s advisable to explore region-specific options if they apply to your situation.
- Energy-Efficient Home Program: This program encourages energy-efficient home construction or renovations. While it might not provide direct financial aid, it can help you reduce long-term homeownership costs by making your home more energy-efficient and sustainable.
What are the down payment rules in Manitoba for homebuyers?
In Manitoba, homebuyers usually need to provide a down payment ranging from 5% to 20% of the property’s purchase price. Consider government assistance programs for Manitoba mortgages, such as the First-Time Home Buyer’s Tax Credit, to help you accumulate the necessary funds.
How does the Manitoba housing market affect mortgage qualification?
The state of the Manitoba housing market can significantly influence your mortgage qualification process. In competitive markets, you may need to act quickly to secure a mortgage and make a strong offer on a property. Staying informed about the Manitoba Housing Market Analysis can give you an advantage in navigating the real estate landscape and securing a favourable mortgage rate.
What are the steps in the Manitoba mortgage application process?
The Manitoba mortgage application process involves several steps, starting with Mortgage pre-approval. During this process, you’ll work with a mortgage broker in Manitoba to assess your financial situation and determine the maximum loan amount you can secure. Then, you’ll move on to house hunting, mortgage approval, and finally, closing the deal. Staying informed about Manitoba mortgage rate trends throughout these steps can help you secure the best possible rates and terms.
What is the average mortgage rate in Manitoba?
As of recent data, the average mortgage rate in Manitoba ranges from 2.5% to 3.5% for a fixed-rate mortgage. Variable rates may vary more, depending on the lenders and the current real estate market in Manitoba.
The Role of Mortgage Brokers in Manitoba’s Homebuying Landscape
“Should I use a mortgage broker in Manitoba?” This question often arises when individuals embark on their homebuying journey. Mortgage brokers serve as valuable assets, providing expert guidance and support throughout the complex process of qualifying for a mortgage in Manitoba. They can connect you with mortgage lenders who offer terms that match your unique financial situation. In addition to their matchmaking role, a mortgage broker can also be your trusted guide, walking you through the intricacies of the mortgage application process, helping you gather the necessary documents, fill out the paperwork, and ensure a smooth application process. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or a seasoned homeowner, enlisting the services of a mortgage broker can prove to be a wise decision in navigating the sometimes daunting world of mortgages.
In summary, achieving mortgage eligibility in Manitoba involves understanding crucial factors such as credit scores, income verification, and the local housing market. By following essential tips and utilizing government assistance programs, you can enhance your prospects of homeownership in this picturesque province.
Mortgages! It’s a term that conjures up images of dream homes and the financial stepping stones to achieve them. But how much do we understand about the terms and rates attached to them, especially in the context of Canada? Let’s start by unraveling the mortgage basics.
Mortgage Rates and Terms
Interest Rates Explanation: These are the interest rates you’ll pay on your home loan. They can fluctuate due to various factors, so it’s essential to understand what drives these changes.
Loan Terms Definition: This refers to the length of time you commit to a specific mortgage rate and lender. Common loan term options are 15, 20, and 30 years. The length of your term affects your monthly payments and the total interest you’ll pay.
Now we’ll answer all the questions you may have about mortgage rates and terms.
1. What Are Current Mortgage Rates in Canada?
At present, current mortgage rates in Canada fluctuate based on various economic indicators and the policies of the Bank of Canada. Keeping an eye on the Canadian housing market and mortgage rates provides a clear picture of the real estate scenario and where it might be headed.
As of the latest update, the Bank of Canada has held its benchmark interest rate steady at a notable five percent.
Understanding mortgage rates is not just about knowing the current percentages. It’s also essential to recognize the different components, such as fixed vs. variable rate mortgages. For instance, while a fixed rate ensures that your interest doesn’t change over a set period, variable rates can shift based on market conditions.
2. What Factors Affect Mortgage Rates in Canada?
Several factors influence mortgage rates in Canada, including:
- Economic Conditions: The overall state of the Canadian economy, inflation rates, and employment numbers can impact mortgage rates.
- Bank of Canada Policies: The central bank’s benchmark interest rate, which is set based on economic conditions, has a direct effect on mortgage rates. When the Bank of Canada raises or lowers its rate, it often leads to corresponding changes in mortgage rates.
- Government Regulations: Government policies and regulations can affect mortgage rates and lending practices. For instance, changes in mortgage stress test requirements can impact the availability of mortgages and their rates.
- Global Economic Factors: Global events and economic conditions can influence Canadian mortgage rates, as they affect the country’s economic stability and borrowing costs.
3. How Do Canadian Mortgage Rates Compare to Other Countries?
Canadian mortgage rates, like those of any country, fluctuate based on a variety of factors including monetary policy, inflation rates, and economic conditions. To make a meaningful comparison of Canadian mortgage rates to those of other countries, one must consider the timeframe and specific economic conditions in question. However, if we take March 2023 we can say that Canada’s mortgage rate in March was 4.50%. This is:
- Higher than the rates in the UK, South Korea, Hungary, Lithuania, Chile, and Norway.
- Lower than the rates in Brazil, Romania, Poland, Australia, Latvia, and the United States.
4. Can I Get a Fixed-Rate Mortgage in Canada?
Fixed-rate mortgages are quite popular in Canada and offer borrowers the security of knowing that their interest rate will remain constant for a specified term, typically 1 to 10 years or even longer. The most common term is a five-year mortgage term.
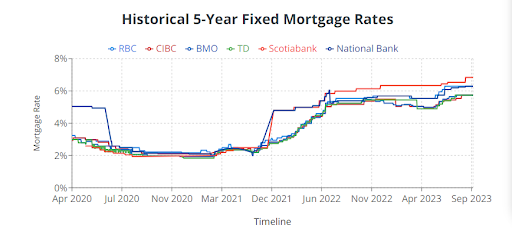
Source from: Wowa.ca
This stability can be advantageous for budgeting because your monthly mortgage payments won’t fluctuate with interest rate changes during the term. What about variable-rate mortgages?
5. Are Variable Mortgage Rates a Good Choice in Canada?
Variable mortgage rates can be a good choice for some borrowers in Canada, depending on their risk tolerance and financial situation. Here is the forecast of variable rate mortgages from 2023 to 2029:
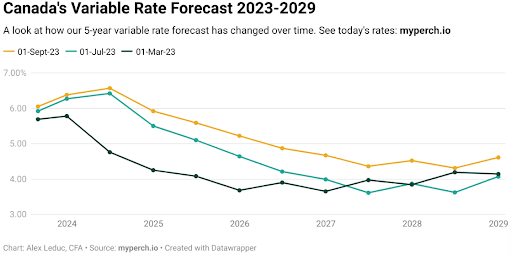
Source from: Myperch.io
Variable rates are tied to the Bank of Canada’s benchmark interest rate and can fluctuate over time. When the central bank lowers its rate, variable mortgage rates can decrease, leading to lower monthly payments. However, they can also increase when the central bank raises its rate.
If you choose a variable rate, it’s important to be financially prepared for potential interest rate hikes in the future. Some borrowers prefer the predictability of fixed-rate mortgages, while others may opt for variable rates to take advantage of potential savings during periods of low-interest rates.
In this note, let’s check the main differences between these two types of mortgage terms.
Fixed vs. Variable Rate Mortgages
Meet Sarah and David, two prospective homebuyers in Canada with different mortgage strategies:
Sarah’s Story — The Fixed-Rate Advocate:
Sarah values stability and predictability in her budget. She opts for a fixed-rate mortgage, locking in a 5-year term at a 3.5% interest rate. Here’s how this decision benefits her:
- Stable Monthly Payments: With a fixed-rate mortgage, Sarah’s interest rate remains constant throughout the entire 5-year term. This means her monthly mortgage payments stay the same, providing predictability and stability for her budget.
- Long-Term Planning: Sarah prefers long-term financial planning and appreciates knowing exactly how much she’ll owe each month. This stability proves valuable during periods of rising interest rates.
- Rate Protection: Even if interest rates in the broader economy rise, Sarah’s mortgage rate and payments won’t be affected. She enjoys peace of mind, knowing her budget won’t be disrupted. However, Sarah should be aware of the potential downsides, such as slightly higher initial rates and penalties for early repayment.
David’s Story — The Variable-Rate Enthusiast:
David is comfortable with a bit of risk and believes interest rates will remain low. He chooses a variable-rate mortgage tied to the Bank of Canada’s benchmark rate. Here’s why David favors this option:
- Initial Lower Rates: David secures a lower initial interest rate of 2.75%, resulting in lower monthly payments compared to fixed-rate options. This aligns with his budget and offers immediate savings.
- Potential for Savings: If interest rates remain stable or decrease over time, David may benefit from lower overall interest costs compared to those with fixed-rate mortgages.
- Flexibility: Variable-rate mortgages often provide more flexibility in making extra payments or paying off the mortgage early without penalties. However, David is also aware of the potential risks, including the uncertainty of future payments if interest rates rise significantly.
These two scenarios highlight how different mortgage types can suit various financial situations and goals. Your choice between fixed and variable rates should align with your unique circumstances and preferences, just like Sarah and David’s decisions did.
Example: Which One Is Right for You?
Choosing between a fixed-rate and variable-rate mortgage depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. Here are some considerations:
- If you value stability and predictability in your budget, a fixed-rate mortgage is a better choice.
- If you believe interest rates will remain low or are comfortable with the potential for rate fluctuations, a variable-rate mortgage may save you money in the long run.
- You can also consider a hybrid mortgage, which combines elements of both fixed and variable rates, providing some stability and potential cost savings.
- Consult with a mortgage advisor or financial planner to evaluate your specific circumstances and determine which mortgage type aligns best with your needs and financial goals.
6. Where Can I Find the Best Mortgage Rates in Canada?
To find the best mortgage rates in Canada, you can start by comparing offers from various lenders, including banks, credit unions, and mortgage brokers. Many mortgage brokers in Canada have online tools that allow you to get rate quotes and compare different mortgage products. Additionally, it’s a good idea to consult with a mortgage broker who can help you navigate the options and find competitive rates tailored to your specific financial situation and goals.
We can help you navigate the myriad of options and locate competitive rates that are tailored to your unique financial situation and objectives.
7. What Are the Typical Mortgage Term Lengths in Canada?
In Canada, typical mortgage term lengths range from 1 year to 25 years, with 5-year terms being the most common. Shorter-term mortgages often have lower interest rates but require more frequent renewals, while longer-term mortgages provide rate stability over a more extended period but may have slightly higher rates.
8. How Does the Bank of Canada Influence Mortgage Rates?
The Bank of Canada plays a significant role in influencing mortgage rates in Canada. It sets the target for its overnight lending rate, which serves as a benchmark for other interest rates in the economy, including mortgage rates. When the Bank of Canada raises or lowers its overnight rate, it directly impacts the interest rates offered by banks and other lenders, affecting the cost of borrowing for consumers.
9. What Should I Know About Mortgage Rate Fluctuations in Canada?
Mortgage rates in Canada can fluctuate over time due to changes in economic conditions, central bank policies, and global events. It’s crucial to understand that these fluctuations are a normal part of the financial market. To mitigate the impact of rate changes, consider your risk tolerance, financial stability, and long-term financial goals when choosing between fixed and variable-rate mortgages.
10. What Are the Steps to Qualify for a Mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying for a mortgage in Canada involves several steps, including:
- Assessing Your Finances: Determine your budget, credit score, and down payment capability.
- Choose a Lender: Research lenders and get pre-approved for a mortgage to understand your borrowing capacity.
- Find a Property: Work with a real estate agent to find a property that suits your needs and budget.
- Complete the Application: Submit a mortgage application to the lender of your choice.
- Undergo a Mortgage Approval Process: The lender will review your financial information, credit history, and the property’s appraisal before approving the mortgage.
- Secure Insurance (if required): If your down payment is less than 20%, you’ll need mortgage insurance through the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) or a private insurer.
- Close the Mortgage: Finalize the mortgage terms, sign the documents, and take possession of the property.
By navigating the nuances of mortgage rates in Canada and monitoring mortgage rate trends, prospective homeowners can navigate the property market with greater assurance.
Ready to take the next step in your home-buying journey? Contact us for personalized mortgage guidance tailored to your unique needs.
So, you’ve decided to take the exciting step towards homeownership in Canada. You’ve familiarized yourself with the basic concepts of mortgages through our previous blog post on mortgage basics, and now you’re ready to dive deeper into the process of qualifying for a mortgage. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or a seasoned investor, understanding the intricacies of Canadian mortgage qualifications is essential to your success.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the key factors that determine your eligibility for a mortgage in Canada. From deciphering credit scores and debt-to-income ratios to unraveling the complexities of down payment requirements, we’ve got you covered. But it doesn’t stop there—our journey continues as we navigate the often-misunderstood landscape of the mortgage stress test, shed light on self-employed mortgage qualifications, and uncover the array of incentives available for first-time homebuyers.
Understanding Canadian Mortgage Qualifications
For anyone looking to secure a mortgage in Canada, understanding the qualification criteria is the first crucial step. Here’s a deeper dive into what lenders typically consider:
Credit Score: The credit score acts as a reflection of your creditworthiness. While a score of 680 or above is often seen as favorable for mortgage approval, many lenders are willing to consider applicants with a score of 650. However, it’s worth noting that the minimum credit score required by default insurers is 600. Those with a score below the preferred range might still get approval, but possibly at higher interest rates.
Debt-to-Income Ratio: This ratio represents how much of your income is dedicated to paying off debts. In Canada, the Gross Debt Service (GDS) ratio—which includes mortgage payments, property taxes, heating expenses, and 50% of condo fees—should not exceed 39%. The Total Debt Service (TDS) ratio, which incorporates all other debt payments, should be 44% or less. Alternate lenders, however, might offer more flexibility in these percentages.
Income Verification: Lenders will scrutinize your income to ensure you can manage the mortgage payments. For those with guaranteed income, even a job that’s as recent as one month can be considered. However, for individuals with fluctuating incomes, such as freelancers or self-employed individuals, a history of two years is typically required. To verify income, lenders might ask for several documents including:
- T4 slips from the last two years
- A recent letter of employment confirming your position, salary, and tenure
- A recent pay stub
- Bank statements showing the deposit of your pay.
Down Payment: The amount you can put down initially can significantly influence your mortgage approval. While it wasn’t explicitly mentioned in your comment, it’s crucial to note that in Canada, the minimum down payment can range from 5% to 20% based on the property’s price. The larger the down payment, the more favorable the loan terms might be.
Down Payment Requirements in Canada and the Mortgage Stress Test
One of the frequently asked questions among potential homebuyers in Canada is, “What is the minimum down payment required for a home loan?” Typically, the down payment requirement starts at 5% for homes priced up to $500,000. However, for properties beyond this price point, an additional consideration comes into play. The down payment is 10% on the portion of the home’s price that exceeds $500,000. For instance, if you’re purchasing a house for $550,000, the calculation would be $500,000 x 5% ($25,000) plus $50,000 x 10% ($5,000), resulting in a total down payment of $30,000. Furthermore, when the property’s purchase price surpasses $1,000,000, the minimum down payment becomes 20% or more.
Moreover, most lenders require a history of the down payment over the past 90 days. This history can be documented through bank statements or other appropriate means, offering transparency and reassurance to lenders regarding the source and stability of the funds.
Another pivotal aspect of Canadian mortgage eligibility centers around the mortgage stress test. This test is a crucial tool utilized by federally regulated lenders to gauge whether a borrower can comfortably manage their mortgage payments should interest rates rise. To qualify, borrowers must demonstrate their ability to meet their loan obligations at the higher of either 5.25% or 2% more than the interest rate offered by the lender. This stress test serves as a safety measure, ensuring that borrowers have a financial cushion against potential economic uncertainties.
Self-Employed Mortgage Qualification and First-Time Homebuyer Incentives
For self-employed individuals seeking clarity on the specific requirements to secure a mortgage in Canada, it’s important to recognize that while the process might involve additional complexities, a range of lenders specifically caters to self-employed professionals. Demonstrating a stable income becomes a pivotal factor, and meeting the standard qualification criteria—such as maintaining a satisfactory credit score and adhering to a healthy debt-to-income ratio—remains essential.
Typically, lenders often request a two-year history of income to ascertain financial stability for self-employed applicants. However, it’s noteworthy that certain specialized programs offer an accelerated path, allowing individuals to qualify for a mortgage as soon as six months after becoming self-employed.
In terms of documentation, self-employed individuals typically need to provide Notices of Income Tax assessment for the previous two years. Additionally, bank statements, business financial statements, and a complete T1 tax return form are often required to provide lenders with a comprehensive view of financial stability and creditworthiness.
First-time homebuyers in Canada are presented with unique opportunities as well. Various programs and incentives, including the First-Time Home Buyer Incentive and the Home Buyers’ Plan, are designed to alleviate the financial strain associated with purchasing a home.
Mortgage Pre-Approval and Affordability Calculations in Canada
Applying for a mortgage in Canada involves a vital preliminary step known as pre-approval. During this process, a potential lender reviews your financial situation and provides an estimate of the maximum mortgage amount you could qualify for. This pre-approval isn’t a guarantee of a final mortgage approval, as changes in your financial situation or property details can affect the final decision.
Meanwhile, calculating your mortgage affordability can help you identify your price range for house hunting. Various online tools, like the mortgage affordability calculator in Canada, can assist you in this. These calculators consider your income, existing debts, property taxes, and expected mortgage interest rate to estimate how much mortgage you can comfortably afford.
However, these tools are meant to provide estimates and should not be used as a definitive guide. The actual amount you can afford may differ depending on various other factors, including the mortgage approval guidelines in Canada and your personal comfort level with housing expenses. To navigate these complexities, it’s advisable to consult with a mortgage professional or financial advisor.
Understanding how to qualify for a mortgage in Canada is a crucial step in the home buying journey. It involves recognizing the Canadian mortgage eligibility criteria, including credit scores, debt-to-income ratio, down payment requirements, and the type of mortgage that suits your financial condition and risk tolerance. It’s also about knowing how to navigate the Canadian home loan approval process and utilizing available tools like mortgage affordability calculators. The process might seem complex, but with thorough preparation and possible assistance from mortgage professionals, you can position yourself for successful mortgage approval. Always remember, the ultimate goal is to secure a mortgage that matches your financial capacity and homeownership dreams. With the right steps, your path to a successful home buying experience in Canada becomes clearer and more attainable.
Welcome back to our journey into the world of mortgages in Canada! In our previous blog post, we took the first steps towards understanding the basics of mortgages, paving the way for your entry into the realm of homeownership. Now, get ready to delve deeper into the fascinating array of mortgage options that Canada has to offer. Think of it as exploring a treasure trove of opportunities, each with its unique benefits and purposes, designed to match your specific needs. Whether you’re on the brink of buying your dream home, considering a cozy vacation getaway, or contemplating refinancing, this guide will serve as your trusty map to navigate the intricate landscape of mortgage types in Canada.
Residential Mortgages
Residential mortgages stand as a cornerstone in Canada’s housing market, representing the primary method for many Canadians seeking homeownership. Recent statistics indicate that over 70% of Canadians depend on financing to purchase their homes, a testament to the essential role these mortgages play in the country’s real estate dynamics. Typically featuring competitive interest rates and extended tenures, residential mortgages make monthly repayments more achievable for a vast majority. One distinguishing characteristic of these mortgages is the fixed-rate option. This ensures that the interest rate remains unwavering throughout the term. As a result, homeowners can breathe easy, secure in the knowledge that their monthly payments will remain steady, irrespective of any economic fluctuations or changing financial climates.
Commercial Mortgages
A commercial mortgage is a specialized loan product designed for businesses and investors to purchase, develop, or refinance commercial properties. Unlike residential mortgages, which are typically made to individual borrowers for homes, commercial mortgages are often secured by covering a diverse range of property types, including but not limited to:
Places of Worship: Secure financing for religious institutions and places of worship to support their community-driven initiatives.
Gas Station: Fuel the growth of your gas station business with our specialized mortgage solutions.
Nursing/Retirement Home: Invest in or upgrade nursing or retirement homes to ensure the well-being of elderly residents.
Industrial Mall: Expand your industrial business operations by acquiring or developing industrial mall spaces.
Commercial Retail Property: Finance retail spaces and shopping complexes to create thriving commercial hubs.
Office: Acquire office spaces or refinance existing ones to support your business operations.
Mixed-Use: Secure funding for properties that combine commercial and residential spaces in a single development.
Multi-Residential: Invest in multi-family apartment complexes to provide valuable housing options.
Rural and Agricultural Mortgages
Rural and agricultural mortgages are tailored loan solutions designed for individuals and businesses operating in less densely populated areas, emphasizing the unique financial demands of the farming and agribusiness sectors. These mortgages facilitate the purchase, development, or refinancing of rural lands, farms, and related agricultural facilities. Given the distinctive nature of farming, factors such as soil quality, type of crops grown, and water availability play a pivotal role in the mortgage terms.
Equipment Financing
An indispensable aspect of modern agriculture is the reliance on machinery and equipment. Recognizing this, many financial institutions offer specialized equipment financing options. These options ensure that farmers and agribusinesses can acquire, upgrade, or maintain essential machinery. Such dedicated financing plays a pivotal role in driving efficiencies, promoting sustainable practices, and ultimately, ensuring that rural and agricultural entities remain competitive in a swiftly changing market. These loans typically require a down payment of 20% or more. Successfully obtaining this form of financing demands specialized knowledge. Fortunately, we are experts in this niche. For guidance and more details, contact us — we specialize in assisting clients with this unique mortgage type.
Reverse Mortgages
Designed primarily for senior Canadians, reverse mortgages present a distinctive opportunity. Homeowners can access a portion of their home’s equity in cash, eliminating the need to relocate or handle monthly repayments. The amount is eventually settled, typically from the sale proceeds when the homeowner chooses to sell or upon their passing. It’s worth noting that only a few lenders offer this specialized mortgage type, and we are proud to be among the experts in this field. For more details or to explore this mortgage option further, please contact us.
Construction Mortgages
A construction mortgage is a boon for those passionate about crafting a home suited to their unique preferences. Instead of a lump sum amount, the funds are released in stages, corresponding with the construction’s progress, a process commonly referred to as “Draws.” This approach guarantees financial discipline and optimizes the construction journey. Notably, if the land on which the house is being built is already paid off, its value can be utilized as the down payment, further easing the financial requirements. Once the construction reaches completion, the mortgage can typically be transitioned into a standard residential mortgage.
Vacation and Second Home Mortgages
The allure of a vacation home, nestled amidst Canada’s scenic landscapes, is undeniable. This specialized mortgage type facilitates the acquisition of second homes or vacation properties. While the approval criteria might be stricter given the nature of the investment, it’s noteworthy that the down payment for a second home doesn’t necessarily have to be substantial. In fact, it can be as low as 5 to 10 percent. For those who can navigate these requirements, a serene retreat in the heart of Canada’s beauty awaits.
Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC)
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) can be visualized as a financial reservoir. At its core, it is a credit line that leverages the equity built up in your home. Before delving deeper into the mechanics of a HELOC, it’s crucial to understand “equity.” In simple terms, home equity is the current market value of your home minus any outstanding mortgage balance. It represents the portion of the home you truly own, as opposed to what you still owe the bank.
Let’s consider an example. If your home is currently worth $300,000 and you have a remaining mortgage balance of $150,000, then your home equity is $150,000.
With a HELOC, homeowners can typically access up to 80% of their home’s market value, less any outstanding mortgage balance. So, in the above example, 80% of $300,000 is $240,000. Once you subtract the mortgage balance of $150,000, you can potentially access a HELOC of up to $90,000.
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) offers homeowners the flexibility to borrow funds as and when required, making it an invaluable tool for unexpected expenses or extensive home renovation projects. What sets HELOC apart is its revolving credit feature: homeowners can borrow, repay, and re-borrow as necessary. This fluidity provides individuals with enhanced financial adaptability, empowering them to adeptly navigate their financial landscape in response to evolving needs.
Interim Financing
The world of real estate is often about timing. Interim financing, commonly known as bridge loans, provides a financial bridge for homeowners caught between the sale of their current home and the purchase of a new one. This short-term financing ensures that homeowners don’t miss out on a potential dream home due to timing mismatches.
Renovations and Home Improvement Mortgages
Your home is more than just a structure; it’s a reflection of your tastes, and understandably, those tastes can evolve over time. In Canada, the “purchase plus improvement” program offers a unique advantage to homebuyers. This program permits buyers to not only secure financing for the purchase of their homes but also acquire additional funds from lenders for significant improvements. Whether it’s adding a new room, overhauling the entire interior design, or making essential repairs, the program ensures that homeowners have the resources to shape their homes in line with their visions. Remarkably, this can be done with as low as a 5% down payment, making it accessible to a broader range of potential homeowners. These mortgages, therefore, provide both the foundation for homeownership and the financial impetus for those dreaming of tailoring their new homes to their evolving preferences.
Convertible Mortgages
A convertible mortgage offers the flexibility to change the type of mortgage during its term. For instance, you can start with a variable rate and then switch to a fixed rate. This type of mortgage is beneficial for those who want to take advantage of current low rates but anticipate rates might rise in the future.
Lender Types
Private mortgages are defined more by the nature of the lender rather than the borrower or the type of property being financed. Whether residential, commercial, or another type of property, the lending landscape is diverse. Most of the mortgage types listed above may be financed by three different types of lenders, which are as follows:
- Prime Lenders: Often referred to as “A lenders”, these are the mainstream banks and financial institutions that most people are familiar with. They usually offer the lowest interest rates and favourable terms, but they have stringent criteria for approval. Borrowers need to have a strong credit history, consistent income, and typically, a considerable down payment to qualify for loans from prime lenders.
- Alternate Lenders (B Lenders): These are institutional lenders who operate in spaces where traditional banks might not. They are willing to work with borrowers who might have minor credit issues or non-traditional income streams. While they might offer slightly higher interest rates compared to prime lenders, they fill a crucial gap in the lending market for those who don’t quite fit the mould for mainstream financing but still have relatively stable finances.
- Private Lenders: These lenders offer the most flexibility, catering to a diverse range of borrowers, including those with significant credit challenges, fluctuating incomes, or unique property types. Since they are not bound by the regulations that govern traditional banks and financial institutions, they can make decisions based on property values and individual borrower circumstances. However, this flexibility often comes at a cost; interest rates can be substantially higher, terms can be shorter, and a larger down payment might be required.
In conclusion, the diverse mortgage landscape in Canada offers tailored options for various needs. From stable residential mortgages to flexible private mortgages, specialized solutions like reverse mortgages, construction loans, and vacation property mortgages, each choice serves a unique purpose. Bridging solutions, debt consolidation, and renovation mortgages provide practical support, while portable and convertible mortgages offer added flexibility. Understanding these options empowers prospective homeowners to make informed choices aligned with their financial goals and lifestyles.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of mortgages, covering various topics. Our goal is to provide you with a detailed understanding of the mortgage world, empowering you to make informed decisions and navigate the mortgage landscape with confidence. Let’s check the mortgage basics together:
What Is a Mortgage?
A mortgage helps you get financing for buying a home and property. It is a legally binding agreement between the borrower and the lender, typically a bank or financial institution, with the property acting as security for the loan. This means that if the borrower fails to make the required payments, the lender can take possession of the property through a process known as foreclosure.
Here are the parties involved in the mortgage process:
- Borrower:
The individual or individuals seeking to purchase the property and obtain the mortgage.
- Lender:
The financial institution or lender who provides the funds for the mortgage.
- Real Estate Agent:
A licensed professional who assists in the property search and purchase process.
- Mortgage Broker:
A middleman who connects borrowers with lenders and helps with the mortgage application process.
How Mortgages Work in Canada
Understanding how mortgages work is essential to make informed decisions about the most suitable options for your financial situation within the Canadian context. As mentioned earlier, mortgages involve borrowing funds to purchase or refinance a property, but let’s dive deeper into the mechanics:
- Principal: The principal amount is the original loan amount borrowed. As you make regular payments, the principal gradually decreases.
- Interest: Interest is the cost or fee charged for borrowing money, typically expressed as a percentage of the loan amount, which borrowers pay back to lenders along with the principal amount.
- Amortization: The amortization period refers to the total time it takes to repay the mortgage in full. Common amortization periods in Canada are 15, 20, or 30 years.
- Fixed vs. Variable Rates: Understanding mortgage rates and terms is essential for making informed decisions when purchasing a home in Canada. Mortgages in Canada can have fixed interest rates, where the rate remains constant throughout the loan term, providing predictability, or variable rates, which fluctuate based on market conditions after an initial fixed-rate period.
The Mortgage Process in Canada
The journey to obtaining a mortgage in Canada can be divided into several key stages:
- Preparation: Before venturing into the Canadian mortgage market, assess your financial readiness. Check your credit score, review your income and expenses, and determine how much you can comfortably afford to borrow.
- Research and Comparison: Thoroughly research different mortgage options available in Canada, including residential mortgages, private mortgages, and more. Compare interest rates, basic mortgage terms, and conditions to find the best fit for your unique financial situation within the Canadian mortgage landscape.
- Application: Once you’ve identified the ideal mortgage in Canada, submit a comprehensive mortgage application to the lender. The application will require detailed information about your financial status, employment history, and the property you intend to purchase.
- Underwriting: During the underwriting process in Canada, the lender evaluates your creditworthiness and assesses the risk involved in lending to you. They may request additional documents and conduct property appraisals to ensure the property’s value aligns with the loan amount.
- Approval and Closing: Upon approval in Canada, you will receive a loan commitment letter outlining the terms and conditions. After carefully reviewing and signing the necessary documents, the mortgage is funded, and you officially become a homeowner in Canada.
Types of Most Common Mortgages in Canada
In Canada, several types of mortgages cater to different financial needs and circumstances. Here are the most common ones:
1. Residential Mortgages:
These are traditional mortgages used to finance the purchase of a primary residence.
2. Private Mortgages:
Private mortgages are loans provided by individuals or private lenders rather than traditional financial institutions.
3. Reverse Mortgages:
Reverse mortgages are available to seniors and allow them to convert home equity into cash without selling the property.
4. Construction Mortgages:
These mortgages are designed to finance the construction of a new home.
5. Vacation and Second Home Mortgages:
As the name suggests, these mortgages are for purchasing vacation homes or second residences.
6. Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC):
A HELOC allows homeowners to borrow against their home equity on an as-needed basis.
7. Interim Financing:
Interim financing provides short-term funds during the home construction process.
8. Renovations and Home Improvement:
Specific mortgages are available for financing home renovations and improvements.
9. Debt Consolidation and Bridge Financing:
Debt consolidation mortgages combine multiple debts into a single loan, and bridge financing covers the gap between the purchase of a new home and the sale of an existing one.
How to Qualify for a Mortgage in Canada
Qualifying for a mortgage in Canada involves meeting specific eligibility criteria set by lenders and regulators. Here are some key factors that lenders consider:
- Credit Score: A strong credit score demonstrates your creditworthiness and ability to manage debt responsibly. Lenders in Canada typically prefer a credit score of 680 or higher, but some may consider borrowers with lower scores.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lenders assess your debt-to-income ratio, which compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. A lower debt-to-income ratio indicates your ability to handle mortgage payments alongside other financial obligations.
- Employment and Income Stability: A stable employment history and consistent income are essential for mortgage qualification in Canada. Lenders want assurance that you can repay the loan over the long term.
- Down Payment: In Canada, the minimum down payment required is typically 5% for properties with a purchase price of up to $500,000. For homes with a higher price, a larger down payment is required.
- Property Appraisal: The property you intend to purchase must undergo an appraisal to ensure its value aligns with the loan amount.
- Other Financial Factors: Lenders may also consider your assets, liabilities, and any other outstanding loans or financial commitments.
Meeting these qualifications strengthens your chances of securing a mortgage in Canada, allowing you to embark on the journey toward homeownership with confidence.
Here are some other tips to get a mortgage:
- Start by reviewing your credit score and history within the Canadian context. A higher credit score can improve your chances of securing a favourable mortgage.
- Determine how much you can afford to borrow based on your income, expenses, and down payment within Canada. Make use of the basic mortgage calculator in Canada to understand the financial implications of your mortgage.
- Prepare the necessary documentation, including proof of income, bank statements, and tax returns, to support your mortgage application in Canada.
- Understand the mortgage pre-approval process and consider getting pre-approved for a mortgage before house hunting within Canada. Through pre-approval, you can show the lenders that you are a credible and serious homebuyer.
- Complete the mortgage application and submit it to your chosen lender within Canada.
- The lender will conduct underwriting to assess your creditworthiness and the property’s value. Once approved, you’ll move forward to the closing process within Canada.
You’ve now gained extensive knowledge about mortgage options in Canada and the entire mortgage process tailored for Canadian readers. Armed with this information, you can confidently explore different mortgage types, compare lenders, and secure a mortgage that aligns with your financial goals and lifestyle within Canada.
Welcome to our comprehensive mortgage guide on options and financial freedom. In this detailed article, we will delve into the world of mortgages, exploring various types of mortgages, the mortgage process, how to compare mortgages, the reasons people need mortgages, and how to secure a mortgage that suits your needs and preferences.
Whether you are a first-time homebuyer or looking to refinance, understanding mortgages is crucial for making informed decisions and achieving your financial goals. Let’s check this mortgage guide for Canadians.
Mortgage Basics
At its core, a mortgage is a powerful financial tool that enables individuals in Canada to purchase or refinance real estate by leveraging the property as collateral. By entering into a mortgage agreement with a lender, known as the mortgagee, Canadian borrowers, also known as mortgagors, gain access to funds upfront, allowing them to make their homeownership dreams a reality. In return, borrowers commit to repaying the loan over time through regular installments, which consist of both principal and interest payments.
Types of Mortgages
Now, let’s explore the types of most common mortgages in Canada:
-
Residential Mortgages
Residential mortgages are the bedrock of the Canadian housing market, enabling countless individuals to purchase their dream homes. These mortgages often come with lower interest rates and longer terms, making them more affordable for Canadian borrowers. To secure the best possible terms, it’s essential to assess your financial situation and creditworthiness before selecting a residential mortgage in Canada.
-
Private Mortgages
Private mortgages present an alternative option for Canadian individuals who may not qualify for traditional bank loans due to credit issues or non-traditional income sources. These mortgages are funded by private lenders within the Canadian context, and while they may come with higher interest rates, they can be a viable solution for certain situations. Before opting for a private mortgage in Canada, conduct careful consideration and thorough research.
-
Reverse Mortgages
Reverse mortgages cater to seniors aged 55 and older in Canada, offering them the opportunity to convert a portion of their home equity into cash. The unique aspect of reverse mortgages is that they do not require monthly repayments. Instead, the outstanding balance becomes due when the homeowner sells the property, moves out, or passes away. Seniors in Canada can enjoy financial flexibility with a reverse mortgage, but it’s crucial to approach this option with caution, considering potential implications.
-
Construction Mortgages
Construction mortgages cater to those building new homes or undertaking substantial renovations within Canada. These loans are typically released in stages as the construction progresses, ensuring that funds are available when needed. When considering a construction mortgage in Canada, it’s essential to understand the intricacies of the building process, timelines, and budgeting.
-
Vacation and Second Home Mortgages
For those dreaming of a vacation retreat or a second home in Canada, vacation and second home mortgages can turn those dreams into reality. These mortgages have distinct approval processes and may require a higher down payment, but they open up exciting opportunities for property ownership beyond one’s primary residence.
-
Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC)
A home equity line of credit (HELOC) is a revolving line of credit based on the Canadian homeowner’s equity. Borrowers can withdraw funds as needed, making it an excellent option for ongoing expenses or sudden financial needs within Canada. Using a HELOC wisely can be a valuable financial strategy to address various financial requirements.
-
Interim Financing
Interim financing, also known as bridge loans, bridges the gap between the purchase of a new property and the sale of an existing one within Canada. This short-term financing option allows homeowners to secure their new home without rushing the sale of their current one. However, as with any financial product, careful planning and consideration are essential to ensure a seamless transition within the Canadian real estate market.
-
Renovations and Home Improvement Mortgages
Renovations and home improvement mortgages offer financing for home improvement projects within Canada. Homeowners can borrow against their home’s equity or refinance their existing mortgage to fund these improvements, which can enhance the property’s value and comfort.
-
Debt Consolidation and Bridge Financing
Debt consolidation and bridge financing are invaluable tools to manage debt and streamline finances in Canada. Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan, simplifying repayments and potentially lowering the overall interest rate. Bridge financing, as mentioned earlier, provides temporary funds until more permanent financing is secured within the Canadian context.
Factors Affecting Mortgage Rates
Understanding the factors that influence mortgage rates can empower you to secure the best possible deal. Some essential elements that lenders consider include:
1. Credit Score
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining the interest rate you qualify for. A higher credit score signals to lenders that you are a reliable borrower, potentially leading to more favourable rates. Conversely, a lower credit score may result in higher interest rates or even difficulties in obtaining a mortgage.
2. Down Payment
The size of your down payment can impact the mortgage rate. A larger down payment typically indicates a lower risk for the lender, potentially resulting in a reduced interest rate.
3. The Interplay of Economic Factors: Bank of Canada Rate and Bond Yields
Mortgage rates are influenced by broader economic factors such as inflation, unemployment rates, and overall economic stability. In times of economic growth, interest rates may rise, while they tend to lower during economic downturns. However, it’s important to highlight the role of the Bank of Canada rate and bond yields in this dance since they play crucial roles in determining mortgage rates.
Let’s delve into their significance and how they respond to the ebb and flow of the economy:
- Bank of Canada Rate: The Bank of Canada sets the benchmark interest rate for the country. When this rate goes up, commercial banks often raise their prime lending rates. As a result, borrowers might see higher interest rates on variable-rate mortgages and lines of credit.
- Bond Yields: Government bonds are a crucial part of the financial landscape. When investors are uncertain about economic conditions, they often turn to safer investments like government bonds. The demand for bonds increases, which in turn pushes bond prices up and yields down. Mortgage rates, particularly for fixed-rate mortgages, correlate with these bond yields. When bond yields rise, fixed mortgage rates tend to follow suit.
Economic Conditions
Both the Bank of Canada rate and bond yields are strongly linked to the overall economic climate. In times of economic growth, the Bank of Canada might raise rates to prevent excessive inflation. Similarly, investors might demand higher bond yields in uncertain economic times to compensate for perceived risks.
4. Loan Term
The length of your mortgage term can affect the interest rate. Shorter terms often come with lower rates but higher monthly payments, while longer terms may have slightly higher rates but offer more manageable monthly payments.
Choosing the Right Mortgage
Selecting the right mortgage involves careful consideration of your financial situation, risk tolerance, and future plans. Here are some valuable tips to guide you in making an informed decision:
1. Assess Your Financial Health
Before diving into the home-buying process, conduct a thorough assessment of your financial health. Evaluate your credit score, outstanding debts, and current income to determine how much loan amount you can afford.
2. Compare Lenders and Offers: Seek Professional Advice and Compare Your Options
Comparing mortgages in Canada can be overwhelming, but it’s crucial to find the best fit for your financial situation and aspirations. Here are some key factors to consider when comparing mortgages:
- Interest Rates: Understanding mortgage rates and terms is crucial for making informed decisions when obtaining a mortgage. Compare interest rates from different lenders in Canada, including those catering specifically to the Canadian market.
- Loan Terms: Assess the length of the loan term within the Canadian context. Shorter terms often have higher monthly payments but lower total interest costs over time.
- Fees and Closing Costs: Factor in any fees and closing costs associated with the mortgage in Canada. These can vary among lenders and impact the overall cost of borrowing.
- Down Payment Requirements: Different mortgages in Canada have varying down payment requirements. A larger down payment may lead to lower monthly payments and better terms.
- Customer Service and Reputation: Research the lender’s customer service reputation within the Canadian market and read reviews from other Canadian borrowers to ensure a smooth borrowing experience.
At Enrich we do all of these for the clients, saving them headaches and giving them professional advice.
3. GET Pre-Approved
Obtaining a pre-approval letter from a lender can give you a competitive edge in the housing market. It demonstrates to sellers that you are a credible and serious buyer and increases your chances of closing the deal.
4. Seek Professional Advice
Navigating the world of mortgages can be complex, and seeking guidance from a qualified mortgage advisor or financial expert can prove invaluable. They can help you make sense of the various options and find a mortgage that best suits your unique needs.
Achieving Financial Freedom Through Smart Mortgage Management
A mortgage is more than just a loan, it’s a tool that, when used wisely, can pave the way to financial freedom. Here are some strategies to manage your mortgage responsibly:
1. Make Timely Payments
Punctual mortgage payments not only strengthen your credit history but also save you from costly late fees and penalties. Set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure you never miss a due date.
2. Consider Extra Payments
If your financial situation allows, consider making extra payments toward your principal. This can help you pay off your mortgage faster and save on interest over the long term.
3. Refinance Wisely
When interest rates drop, refinancing your mortgage can be a smart move. However, carefully evaluate the costs and benefits before proceeding. Ensure that the new terms align with your financial goals.
4. Avoid Taking on Excessive Debt
While owning a home is a significant achievement, it’s essential to avoid accumulating excessive debt elsewhere. High credit card balances or personal loans can strain your finances and affect your ability to manage your mortgage effectively.
Owning a home and achieving financial freedom are attainable goals with the right approach to mortgages. By understanding the different types of mortgages, the factors influencing interest rates, and making informed decisions, you can set yourself on a path toward a secure and prosperous future. Remember, the journey to homeownership is not just about finding the perfect house, it’s also about finding a mortgage that fits your needs and aligns with your long-term financial objectives. With diligence, research, and careful planning, you can confidently embark on this exciting journey and leave other websites behind with the power of knowledge at your fingertips.