Mortgages! It’s a term that conjures up images of dream homes and the financial stepping stones to achieve them. But how much do we understand about the terms and rates attached to them, especially in the context of Canada? Let’s start by unraveling the mortgage basics.
Mortgage Rates and Terms
Interest Rates Explanation: These are the interest rates you’ll pay on your home loan. They can fluctuate due to various factors, so it’s essential to understand what drives these changes.
Loan Terms Definition: This refers to the length of time you commit to a specific mortgage rate and lender. Common loan term options are 15, 20, and 30 years. The length of your term affects your monthly payments and the total interest you’ll pay.
Now we’ll answer all the questions you may have about mortgage rates and terms.
1. What Are Current Mortgage Rates in Canada?
At present, current mortgage rates in Canada fluctuate based on various economic indicators and the policies of the Bank of Canada. Keeping an eye on the Canadian housing market and mortgage rates provides a clear picture of the real estate scenario and where it might be headed.
As of the latest update, the Bank of Canada has held its benchmark interest rate steady at a notable five percent.
Understanding mortgage rates is not just about knowing the current percentages. It’s also essential to recognize the different components, such as fixed vs. variable rate mortgages. For instance, while a fixed rate ensures that your interest doesn’t change over a set period, variable rates can shift based on market conditions.
2. What Factors Affect Mortgage Rates in Canada?
Several factors influence mortgage rates in Canada, including:
- Economic Conditions: The overall state of the Canadian economy, inflation rates, and employment numbers can impact mortgage rates.
- Bank of Canada Policies: The central bank’s benchmark interest rate, which is set based on economic conditions, has a direct effect on mortgage rates. When the Bank of Canada raises or lowers its rate, it often leads to corresponding changes in mortgage rates.
- Government Regulations: Government policies and regulations can affect mortgage rates and lending practices. For instance, changes in mortgage stress test requirements can impact the availability of mortgages and their rates.
- Global Economic Factors: Global events and economic conditions can influence Canadian mortgage rates, as they affect the country’s economic stability and borrowing costs.
3. How Do Canadian Mortgage Rates Compare to Other Countries?
Canadian mortgage rates, like those of any country, fluctuate based on a variety of factors including monetary policy, inflation rates, and economic conditions. To make a meaningful comparison of Canadian mortgage rates to those of other countries, one must consider the timeframe and specific economic conditions in question. However, if we take March 2023 we can say that Canada’s mortgage rate in March was 4.50%. This is:
- Higher than the rates in the UK, South Korea, Hungary, Lithuania, Chile, and Norway.
- Lower than the rates in Brazil, Romania, Poland, Australia, Latvia, and the United States.
4. Can I Get a Fixed-Rate Mortgage in Canada?
Fixed-rate mortgages are quite popular in Canada and offer borrowers the security of knowing that their interest rate will remain constant for a specified term, typically 1 to 10 years or even longer. The most common term is a five-year mortgage term.
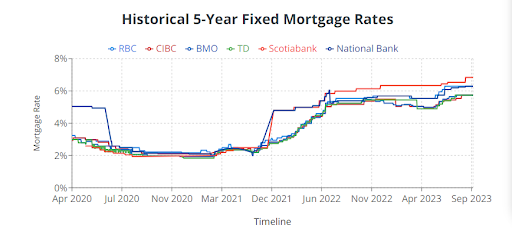
Source from: Wowa.ca
This stability can be advantageous for budgeting because your monthly mortgage payments won’t fluctuate with interest rate changes during the term. What about variable-rate mortgages?
5. Are Variable Mortgage Rates a Good Choice in Canada?
Variable mortgage rates can be a good choice for some borrowers in Canada, depending on their risk tolerance and financial situation. Here is the forecast of variable rate mortgages from 2023 to 2029:
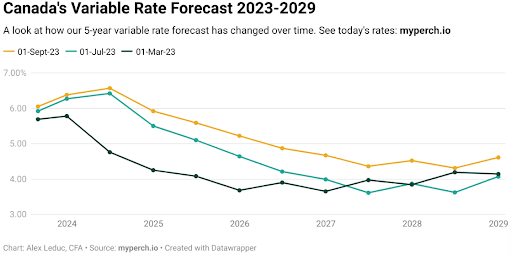
Source from: Myperch.io
Variable rates are tied to the Bank of Canada’s benchmark interest rate and can fluctuate over time. When the central bank lowers its rate, variable mortgage rates can decrease, leading to lower monthly payments. However, they can also increase when the central bank raises its rate.
If you choose a variable rate, it’s important to be financially prepared for potential interest rate hikes in the future. Some borrowers prefer the predictability of fixed-rate mortgages, while others may opt for variable rates to take advantage of potential savings during periods of low-interest rates.
In this note, let’s check the main differences between these two types of mortgage terms.
Fixed vs. Variable Rate Mortgages
Meet Sarah and David, two prospective homebuyers in Canada with different mortgage strategies:
Sarah’s Story — The Fixed-Rate Advocate:
Sarah values stability and predictability in her budget. She opts for a fixed-rate mortgage, locking in a 5-year term at a 3.5% interest rate. Here’s how this decision benefits her:
- Stable Monthly Payments: With a fixed-rate mortgage, Sarah’s interest rate remains constant throughout the entire 5-year term. This means her monthly mortgage payments stay the same, providing predictability and stability for her budget.
- Long-Term Planning: Sarah prefers long-term financial planning and appreciates knowing exactly how much she’ll owe each month. This stability proves valuable during periods of rising interest rates.
- Rate Protection: Even if interest rates in the broader economy rise, Sarah’s mortgage rate and payments won’t be affected. She enjoys peace of mind, knowing her budget won’t be disrupted. However, Sarah should be aware of the potential downsides, such as slightly higher initial rates and penalties for early repayment.
David’s Story — The Variable-Rate Enthusiast:
David is comfortable with a bit of risk and believes interest rates will remain low. He chooses a variable-rate mortgage tied to the Bank of Canada’s benchmark rate. Here’s why David favors this option:
- Initial Lower Rates: David secures a lower initial interest rate of 2.75%, resulting in lower monthly payments compared to fixed-rate options. This aligns with his budget and offers immediate savings.
- Potential for Savings: If interest rates remain stable or decrease over time, David may benefit from lower overall interest costs compared to those with fixed-rate mortgages.
- Flexibility: Variable-rate mortgages often provide more flexibility in making extra payments or paying off the mortgage early without penalties. However, David is also aware of the potential risks, including the uncertainty of future payments if interest rates rise significantly.
These two scenarios highlight how different mortgage types can suit various financial situations and goals. Your choice between fixed and variable rates should align with your unique circumstances and preferences, just like Sarah and David’s decisions did.
Example: Which One Is Right for You?
Choosing between a fixed-rate and variable-rate mortgage depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. Here are some considerations:
- If you value stability and predictability in your budget, a fixed-rate mortgage is a better choice.
- If you believe interest rates will remain low or are comfortable with the potential for rate fluctuations, a variable-rate mortgage may save you money in the long run.
- You can also consider a hybrid mortgage, which combines elements of both fixed and variable rates, providing some stability and potential cost savings.
- Consult with a mortgage advisor or financial planner to evaluate your specific circumstances and determine which mortgage type aligns best with your needs and financial goals.
6. Where Can I Find the Best Mortgage Rates in Canada?
To find the best mortgage rates in Canada, you can start by comparing offers from various lenders, including banks, credit unions, and mortgage brokers. Many mortgage brokers in Canada have online tools that allow you to get rate quotes and compare different mortgage products. Additionally, it’s a good idea to consult with a mortgage broker who can help you navigate the options and find competitive rates tailored to your specific financial situation and goals.
We can help you navigate the myriad of options and locate competitive rates that are tailored to your unique financial situation and objectives.
7. What Are the Typical Mortgage Term Lengths in Canada?
In Canada, typical mortgage term lengths range from 1 year to 25 years, with 5-year terms being the most common. Shorter-term mortgages often have lower interest rates but require more frequent renewals, while longer-term mortgages provide rate stability over a more extended period but may have slightly higher rates.
8. How Does the Bank of Canada Influence Mortgage Rates?
The Bank of Canada plays a significant role in influencing mortgage rates in Canada. It sets the target for its overnight lending rate, which serves as a benchmark for other interest rates in the economy, including mortgage rates. When the Bank of Canada raises or lowers its overnight rate, it directly impacts the interest rates offered by banks and other lenders, affecting the cost of borrowing for consumers.
9. What Should I Know About Mortgage Rate Fluctuations in Canada?
Mortgage rates in Canada can fluctuate over time due to changes in economic conditions, central bank policies, and global events. It’s crucial to understand that these fluctuations are a normal part of the financial market. To mitigate the impact of rate changes, consider your risk tolerance, financial stability, and long-term financial goals when choosing between fixed and variable-rate mortgages.
10. What Are the Steps to Qualify for a Mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying for a mortgage in Canada involves several steps, including:
- Assessing Your Finances: Determine your budget, credit score, and down payment capability.
- Choose a Lender: Research lenders and get pre-approved for a mortgage to understand your borrowing capacity.
- Find a Property: Work with a real estate agent to find a property that suits your needs and budget.
- Complete the Application: Submit a mortgage application to the lender of your choice.
- Undergo a Mortgage Approval Process: The lender will review your financial information, credit history, and the property’s appraisal before approving the mortgage.
- Secure Insurance (if required): If your down payment is less than 20%, you’ll need mortgage insurance through the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) or a private insurer.
- Close the Mortgage: Finalize the mortgage terms, sign the documents, and take possession of the property.
By navigating the nuances of mortgage rates in Canada and monitoring mortgage rate trends, prospective homeowners can navigate the property market with greater assurance.
Ready to take the next step in your home-buying journey? Contact us for personalized mortgage guidance tailored to your unique needs.



